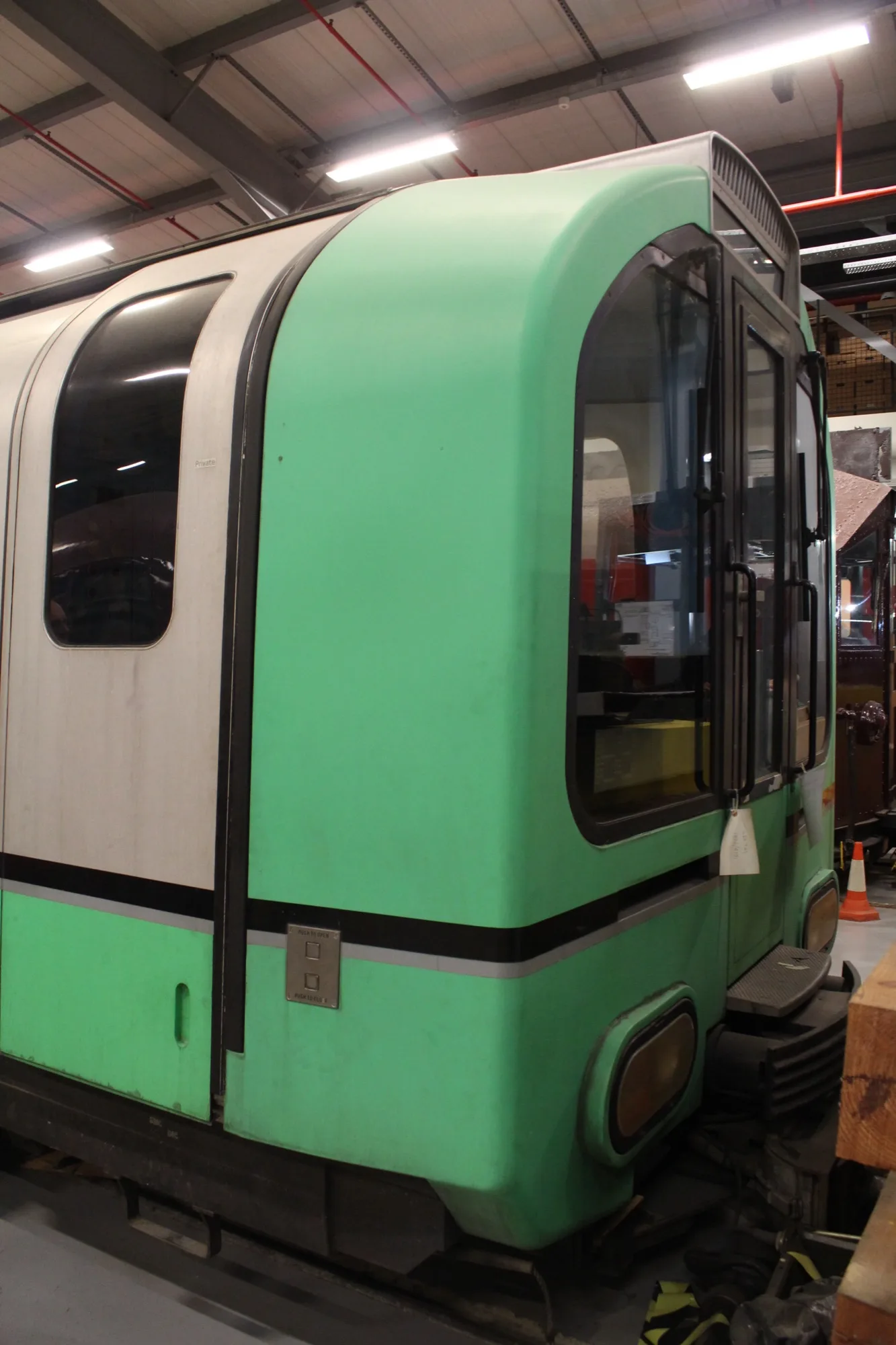
The Central Line of the London Underground is not having a good time at the moment. We experienced this first hand on our recent trip to London. As the Young V&A is close to Bethnal Green tube station, when we visited we tried to use the Central Line to head back into central London.
We gave up after two trains stopped where it was literally impossible to fit on. Every carriage was crush-loaded, and this was mid-afternoon on a Saturday – not exactly rush hour.
The issue is with the trains that run on the Central Line. These are 1992 Stock, which, as the name suggests, date from 1992 and were built by the newly-privatised BREL. Specifically, it’s the traction motors on these trains, which are failing at a faster than expected rate. Without a working motor, the trains can’t move, and so they have to be taken out of service. Consequently, there are fewer trains available for service, and so passengers are being crammed into less frequent services.
Transport for London have short, medium and long-term solutions to this issue:
Short term
In the short term, there are fewer trains in the timetable. With around a third of the fleet out of service, the timetable has been cut to reduce short-term cancellations. It’s something we’ve seen elsewhere in the country – Transpennine Express cut several trains to improve reliability.
Medium term
In the medium term, there is the Central Line Improvement Programme (CLIP). This is a major refurbishment of the trains, which includes replacing the troublesome motors as well as installing CCTV and accessibility improvements. For example, trains will now have wheelchair accessible spaces, and there are new screens with visual announcements of the next stop – standard on other lines, but new to the Central Line.
As an aside, I can’t help but feel that CLIP is a boring name when Central Line Improvement to Train Operation and Reliability Investment Scheme was right there. Even if the acronym does spell CLITORIS.
The CLIP started before the reliability issues came to ahead, and the first refurbished train was in service in December. But it’ll be a while before work on the full fleet of 77 trains is completed.
Long term
Ultimately, these are 30 year old trains, and eventually they will need replacing. They’re not the oldest on the network – that ‘honour’ goes to the Bakerloo Line, with trains that are over 50 years old. Slightly newer, but only just, are those on the Piccadilly Line, which are being replaced with 2024 stock to support an increase in service. Right now, there’s only funding available for new trains for the Piccadilly Line, but TfL’s long term aim is that the same trains will run on the Central, Bakerloo and Waterloo & City Lines too. Whilst the first units are being assembled in Germany and Austria, most will be built by Siemens in a brand new factory in Goole, East Yorkshire.
Where I live in the north of England, a big deal was made out of the replacement of 1980s era Pacer trains which were no longer fit for purpose. And whilst there’s a feeling in the north that London gets more than its fair share of UK public transport spending, the oldest tube trains are 10 years older than the oldest Northern Rail trains. Ordering a completely new fleet for all the London Underground lines that need it will result ensure skilled manufacturing jobs remain in Yorkshire for at least the next decade.